Article Content:
What Is an Electromagnetic Relay Switch?
An electromagnetic relay switch is an electrically operated switch that uses an electromagnetic coil to mechanically open or close electrical contacts. It is one of the most common and essential components in industrial automation, electrical control systems, and consumer electronics.
By isolating control signals from load circuits, electromagnetic relay switches provide a safe, reliable, and low-cost way to manage high-voltage or high-current operations using a low-power control signal.
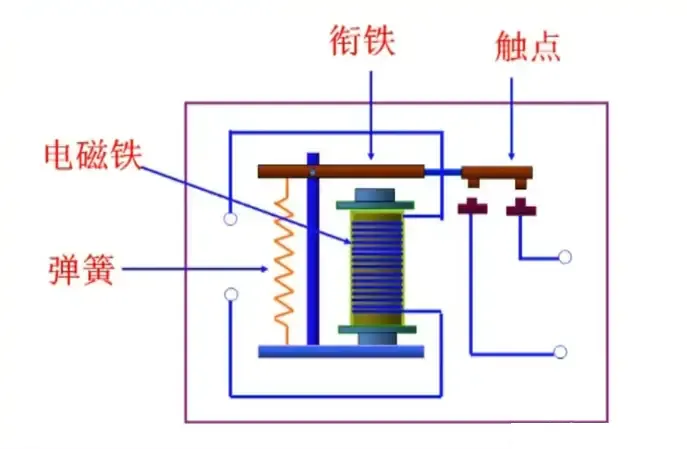
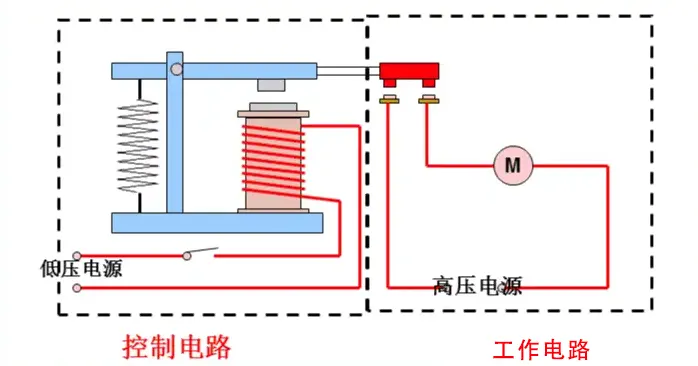
How Does an Electromagnetic Relay Switch Work?
The working principle of an electromagnetic relay switch is based on electromagnetism:
- When a small voltage is applied to the relay coil, it generates a magnetic field.
- This magnetic field pulls a movable armature, which either closes or opens the electrical contacts.
- When the coil is de-energized, a spring mechanism returns the contacts to their original position.
There are typically two contact types:
- Normally Open (NO): Closes when the coil is energized.
- Normally Closed (NC): Opens when the coil is energized.
This simple operation allows the relay to control high power loads (like motors or heaters) from low-voltage logic circuits or microcontrollers.
Types of Electromagnetic Relay Switches
- General Purpose Relays
Used in HVAC, home appliances, and lighting systems. - Power Relays
Designed for switching higher currents and voltages in industrial equipment. - Signal Relays
Optimized for low-current, low-voltage signal control applications. - Time Delay Relays
Provide delayed switching for sequences, lighting, or motor control. - Latching Relays
Maintain their state even after power is removed, suitable for energy-saving systems.
Key Advantages of Electromagnetic Relay Switches
- ✅ Electrical isolation between control and load circuits
- ✅ Low control power, ideal for logic-level devices
- ✅ High switching capacity, handling large AC or DC loads
- ✅ Reliable and cost-effective solution
- ✅ Widely available in various sizes and configurations
Applications of Electromagnetic Relay Switches
- Industrial automation systems
Control motors, solenoids, and other actuators from PLCs or sensors. - Home appliances
Switch compressors, heating elements, or fans. - Automotive systems
Control headlights, fuel pumps, horns, and power windows. - Power distribution panels
Enable circuit protection and automated switching. - Communication equipment
Route signals and manage low-power switching.
How to Choose the Right Electromagnetic Relay Switch
When selecting a relay, consider:
- Coil voltage (e.g., 5V, 12V, 24V DC or 110V AC)
- Contact rating (voltage and current capacity)
- Number and type of contacts (SPST, SPDT, DPDT, etc.)
- Mounting style (PCB, plug-in, DIN rail)
- Environmental resistance (shock, vibration, humidity)
Choosing a quality-certified relay manufacturer ensures durability and consistent performance across all applications.
Conclusion
The electromagnetic relay switch is a foundational technology in electrical engineering, enabling low-power control of high-power systems with safety and efficiency. From household appliances to industrial machinery, this versatile component continues to power innovation across industries. Whether you’re an engineer, technician, or OEM, understanding and using the right electromagnetic relay switch is key to reliable system design.




